构建微服务架构(Ribbon篇)
该篇文档,前置环境条件为:构建微服务架构(eureka篇)
该篇文档,前置代码下载:下载
该篇文档,全部完成后的代码下载:下载
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/u011863024/article/details/114298270
GitHub 地址:https://github.com/Netflix/ribbon
Ribbon 入门介绍
Spring Cloud Ribbon 是基于 Netflix Ribbon 实现的一套客户端负载均衡的工具。
简单的说,Ribbon 是 Netflix 发布的开源项目,主要功能是提供客户端的软件负载均衡算法和服务调用。Ribbon 客户端组件提供一系列完善的配置项如连接超时,重试等。
简单的说,就是在配置文件中列出 Load Balancer (简称 LB )后面所有的机器,Ribbon 会自动的帮助你基于某种规则(如简单轮询,随机连接等)去连接这些机器。我们很容易使用 Ribbon 实现自定义的负载均衡算法。
Ribbon 目前也进入维护模式。
Ribbon 未来可能被 Spring Cloud LoadBalacer 替代。
LB 负载均衡 (Load Balance) 是什么
简单的说就是将用户的请求平摊的分配到多个服务上,从而达到系统的 HA (高可用)。
常见的负载均衡有软件 Nginx,LVS,硬件 F5 等。
Ribbon 本地负载均衡客户端 VS Nginx 服务端负载均衡区别
Nginx 是服务器负载均衡,客户端所有请求都会交给 nginx,然后由 nginx 实现转发请求。即负载均衡是由服务端实现的。
Ribbon 本地负载均衡,在调用微服务接口时候,会在注册中心上获取注册信息服务列表之后缓存到 JVM 本地,从而在本地实现 RPC 远程服务调用技术。
集中式 LB
即在服务的消费方和提供方之间使用独立的 LB 设施(可以是硬件,如 F5, 也可以是软件,如 nginx),由该设施负责把访问请求通过某种策略转发至服务的提供方;
进程内 LB
将 LB 逻辑集成到消费方,消费方从服务注册中心获知有哪些地址可用,然后自己再从这些地址中选择出一个合适的服务器。
Ribbon 就属于进程内 LB,它只是一个类库,集成于消费方进程,消费方通过它来获取到服务提供方的地址。
一句话形容
负载均衡 + RestTemplate 调用
Ribbon 的负载均衡和 Rest 调用
架构说明
总结:Ribbon 其实就是一个软负载均衡的客户端组件,它可以和其他所需请求的客户端结合使用,和 Eureka 结合只是其中的一个实例。
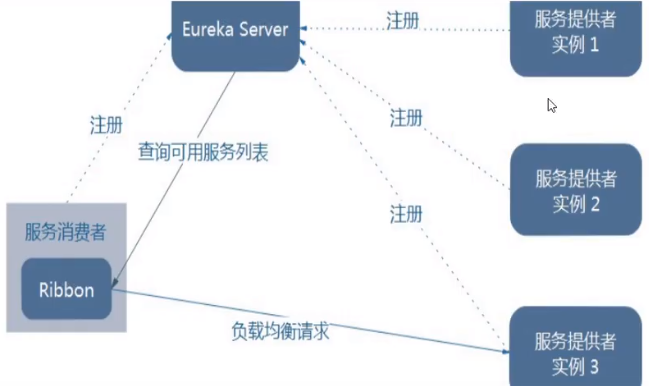
Ribbon 在工作时分成两步:
第一步先选择 EurekaServer ,它优先选择在同一个区域内负载较少的 server。
第二步再根据用户指定的策略,在从 server 取到的服务注册列表中选择一个地址。
其中 Ribbon 提供了多种策略:比如轮询、随机和根据响应时间加权。
POM
先前工程项目没有引入 spring-cloud-starter-ribbon 也可以使用 ribbon。
1 | <dependency> |
这是因为 spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-client 自带了 spring-cloud-starter-ribbon 引用。
RestTemplate 的使用
RestTemplate Java Doc
getForObject() / getForEntity() - GET 请求方法
getForObject():返回对象为响应体中数据转化成的对象,基本上可以理解为 Json。
getForEntity():返回对象为 ResponseEntity 对象,包含了响应中的一些重要信息,比如响应头、响应状态码、响应体等。
1 | @GetMapping("/consumer/payment/getForEntity/{id}") |
postForObject() / postForEntity() - POST 请求方法
Ribbon 默认自带的负载规则
RoundRobinRule 轮询
RandomRule 随机
RetryRule 先按照RoundRobinRule的策略获取服务,如果获取服务失败则在指定时间内会进行重
WeightedResponseTimeRule 对RoundRobinRule的扩展,响应速度越快的实例选择权重越大,越容易被选择
BestAvailableRule 会先过滤掉由于多次访问故障而处于断路器跳闸状态的服务,然后选择一个并发量最小的服务
AvailabilityFilteringRule 先过滤掉故障实例,再选择并发较小的实例
ZoneAvoidanceRule 默认规则,复合判断server所在区域的性能和server的可用性选择服务器
Ribbon 负载规则替换
1. 修改 cloud-consumer-order80
2. 注意配置细节
官方文档明确给出了警告:
这个自定义配置类不能放在 @ComponentScan 所扫描的当前包下以及子包下,
否则我们自定义的这个配置类就会被所有的 Ribbon 客户端所共享,达不到特殊化定制的目的了。
(也就是说不要将 Ribbon 配置类与主启动类同包)
3. 新建 package - com.sevattal.myrule
4. 在 com.sevattal.myrule 下新建 MySelfRule 规则类
1 | package com.sevattal.myrule; |
5. 主启动类添加 @RibbonClient
1 | package com.sevattal.springcloud; |
6. 测试
开启 cloud-eureka-server7001,cloud-consumer-order80,cloud-provider-payment8001,cloud-provider-payment8002
浏览器-输入 http://localhost/consumer/payment/get/1
返回结果中的 serverPort 在 8001 与 8002 两种间反复横跳。
Ribbon 默认负载轮询算法原理
默认负载轮训算法: rest 接口第几次请求数 % 服务器集群总数量 = 实际调用服务器位置下标,每次服务重启动后 rest 接口计数从 1 开始。
List
如:
List [0] instances = 127.0.0.1:8002
List [1] instances = 127.0.0.1:8001
8001+ 8002组合成为集群,它们共计2台机器,集群总数为2,按照轮询算法原理:
当总请求数为1时:1%2=1对应下标位置为1,则获得服务地址为127.0.0.1:8001
当总请求数位2时:2%2=О对应下标位置为0,则获得服务地址为127.0.0.1:8002
当总请求数位3时:3%2=1对应下标位置为1,则获得服务地址为127.0.0.1:8001
当总请求数位4时:4%2=О对应下标位置为0,则获得服务地址为127.0.0.1:8002
如此类推…
RoundRobinRule 源码分析
1 | public interface IRule{ |
1 | package com.netflix.loadbalancer; |
Ribbon 之手写轮询算法
自己试着写一个类似 RoundRobinRule 的本地负载均衡器。
7001/7002 集群启动
1. 8001/8002 微服务改造 - controller
1 | @RestController |
2. 80订单微服务改造
ApplicationContextConfig 去掉注解 @LoadBalanced,OrderMain80 去掉注解 @RibbonClient
1 | import org.springframework.cloud.client.loadbalancer.LoadBalanced; |
创建 LoadBalancer 接口
1 | package com.sevattal.springcloud.lb; |
MyLB 实现 LoadBalancer 接口
1 | package com.sevattal.springcloud.lb; |
OrderController
1 | import org.springframework.cloud.client.ServiceInstance; |
3.测试
不停地刷新 http://localhost/consumer/payment/lb,可以看到 8001/8002 交替出现。


